Cell Phone Radiation Information & Reducing Cellphone EMR Exposure
Please see our full article on this topic found
Excerpts from that article are below
Readers of this article should also
Definition of cellphone radiation - cellular telephones, because they include a radio transmitter, emit electromagnetic fields (EMF, or EMR).
In the United States the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) specifies the allowable limits of cell phone radiation.
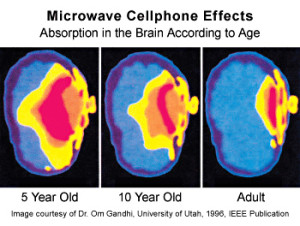
A possible concern is the exposure of the human ear and brain to cellphone radiation, especially as newer digital cell phones operate at higher power and at frequencies in the 1800-2000 MHz range.
Present cell phones may exceed the FCC EMR limit that was set when most cell phones were analog in signal design and emitted lower-strength EMFs in the 800-900 MHz range.(2010 levels DL)
Scientific research on possible health hazards from cellphone use to date (2010) has produced inconclusive and conflicting results, varying by study. According to an article in June 2010 the New York Times,
Both the National Cancer Institute and the F.C.C. [Federal Communications Commission] say that there is no scientific evidence that wireless phones are dangerous, but each agency continues to monitor continuing medical studies. (because they lied or they would have a giant lawsuit and riot on their hands DL)
What type of radiation is emitted by a cellphone? older cell phones emit and receive low level radio frequency waves from 200 MHz to more than 800 MHz. Newer cell phones operate in the 900 MHz to 2.4 GHz or more (approaching the power and frequency of microwaves and infrared waves).
Transmission of signals in the cellphone range are also referred to as UHF or Ultra High Frequency Signals.
Base to Mobile and Mobile to Base Cellphone Frequencies May Differ
It is worth noting that typically the signals that pass between a cell phone and a cell tower are at different frequency ranges depending on the direction of transmission.
For example, a cell phone may transmit from the phone to the cell tower at around 800 MHz, while the tower transmits back to the cellphone at around 1800 MHz.
Because the power level of a cellphone while it is transmitting is very small compared to the power of the cell phone tower when it is transmitting, that means that the stronger of the two cell phone frequencies is the tower transmission signal.
In reading various publications that discuss cell phone frequencies, you may read the cell phone transmit frequency as "mobile to base" and the tower transmit frequency from tower to cell phone as "base to mobile".
Cell Phone Abbreviations and Terms - What Frequencies Your Cell Phone Uses Depend on Your Wireless Carrier as Well as the Phone Itself
AMPS - Advanced Mobile Phone Service - Cell phone industry standard since 1978
Analog service: radio signals modulated to carry information in a continuous signal, like FM radio. Receiver and transmitter use the same frequency.
Digital cell phone service: radio signals are digitized using a binary code (0's and 1's) to convert speech (or any signal sent to or received from a cell phone) to binary data. In the U.S there are 3 wireless technologies: CDMA, TDMA, and GSM.
And of course 1G; 2G; 3G; 3.5G; 4G; 4.5G; and the newest, 5G technology under development in 2019.
TDMA - Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA IS-54) or Digital Amps or D-Amps - since 1994, operates in North America in the 800 MHz band and in the 1900 MHz band, used by AT&T, Bell South, Southwestern Bell.
CDMA - Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA IS-95), in use since th3 1940's, operates at both 800 MHz and 1900 MHz bands, used in the U.S. primarily by Verizon Wireless, and Sprint/Nextel, though CDMA is also used by other carriers including Cricket, MetroPCS, and U.S. Cellular.
CDMA was a proprietary standard developed by Qualcomm in the U.S. EV-DO being developed for CDMA networks (CDMA2000) provides faster data download speeds, similar to DSL in speed.
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications - an improved version of TDMA, adopted first in Europe by 1987, uses wider signal channels (200 KHz) than TDMA. GSM 1900 is used by Aerial, Bell South, Microvcell, Omnipoint, Pacific Bell, Spring Spectrum, Western Wireless. EDGE being developed for GSM networks provides faster data download speeds, similar to DSL in speed.
- 800 MHz band authorized by the U.S. FCC in 1987 for cellphone use.
PCS - Personal Communications Services - 1.9 GHz all digital transmission and reception authorized by the U.S. FCC
SIM cards - Subscriber Identity Module cards are small printed circuit boards that contain individual cell phone account information and that are inserted into GSM phones (in the U.S.).
Because the SIM card contains the user information, cellphones that accept SIM cards become generic - you can move your cell phone account to a new telephone by inserting your SIM card into a new phone, or you can change your cell phone to a different service provider (and telephone number) by buying and inserting a different SIM card into your existing GSM phone.

