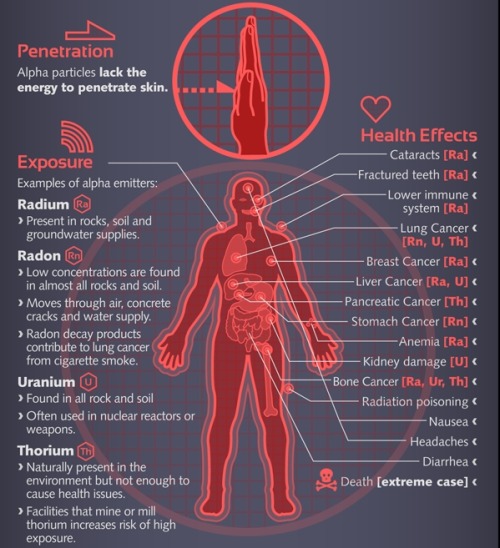
radiation poisoning



Treatment of acute radiation syndrome is generally supportive care. This may include blood transfusions, antibiotics, colony-stimulating factors, or stem cell transplant. If radioactive material remains on the skin or in the stomach it should be removed.
Other names: Radiation poisoning, radiation si...
Causes: Large amounts of ionizing radiation o...
Treatment: Supportive care (blood transfusions, ...
Types: Bone marrow syndrome, gastrointestinal ...
Large doses of ionizing radiation in a short time period lead to Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS), aka radiation poisoning. ... Between 4 and 8 Gy, however, a dose can be fatal—but the route to death still varies on the level of the exposure. Patients at this level suffer vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and fever.26 Jul 2012
If you're exposed to significant radiation, your thyroid will absorb radioactive iodine (radioiodine) just as it would other forms of iodine. The radioiodine is eventually cleared from the body in urine. If you take potassium iodide, it may fill "vacancies" in the thyroid and prevent the absorption of radioiodine.22 May 2019019

