Portal:Ancient Egypt
Portal topics ActivitiesCultureGeographyHealthHistoryMathematicsNaturePeoplePhilosophyReligionSocietyTechnologyRandom portal
THE ANCIENT EGYPT PORTAL
Showcased content about Ancient Egypt
The golden funeral mask of king Tutankhamun, a symbol for many of ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was a civilization of ancient North Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River, situated in the place that is now the country Egypt. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology) with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Menes (often identified with Narmer). The history of ancient Egypt occurred as a series of stable kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age.
Egypt reached the pinnacle of its power in the New Kingdom, ruling much of Nubia and a sizable portion of the Near East, after which it entered a period of slow decline. During the course of its history Egypt was invaded or conquered by a number of foreign powers, including the Hyksos, the Libyans, the Nubians, the Assyrians, the Achaemenid Persians, and the Macedonians under the command of Alexander the Great. The Greek Ptolemaic Kingdom, formed in the aftermath of Alexander's death, ruled Egypt until 30 BC, when, under Cleopatra, it fell to the Roman Empire and became a Roman province.
The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River valley for agriculture. The predictable flooding and controlled irrigation of the fertile valley produced surplus crops, which supported a more dense population, and social development and culture. With resources to spare, the administration sponsored mineral exploitation of the valley and surrounding desert regions, the early development of an independent writing system, the organization of collective construction and agricultural projects, trade with surrounding regions, and a military intended to assert Egyptian dominance. Motivating and organizing these activities was a bureaucracy of elite scribes, religious leaders, and administrators under the control of a pharaoh, who ensured the cooperation and unity of the Egyptian people in the context of an elaborate system of religious beliefs.[1]
The many achievements of the ancient Egyptians include the quarrying, surveying and construction techniques that supported the building of monumental pyramids, temples, and obelisks; a system of mathematics, a practical and effective system of medicine, irrigation systems and agricultural production techniques, the first known planked boats, Egyptian faience and glass technology, new forms of literature, and the earliest known peace treaty, made with the Hittites. Ancient Egypt has left a lasting legacy. Its art and architecture were widely copied, and its antiquities carried off to far corners of the world. Its monumental ruins have inspired the imaginations of travelers and writers for centuries. A newfound respect for antiquities and excavations in the early modern period by Europeans and Egyptians led to the scientific investigation of Egyptian civilization and a greater appreciation of its cultural legacy. (Full article...)
Selected article
Ancient Egyptian literature is literature written in the Egyptian language from Ancient Egypt's pharaonic period until the end of Roman domination. It represents the oldest corpus of Egyptian literature. Along with Sumerian literature, it is considered the world's earliest literature.
It is possible that the overall literacy rate was less than one percent of the entire population. The creation of literature was thus an elite exercise, monopolized by a scribal class attached to government offices and the royal court of the ruling pharaoh. However, there is no full consensus among modern scholars concerning the dependence of ancient Egyptian literature on the sociopolitical order of the royal court. Ancient Egyptian literature has been preserved on a wide variety of media. This includes papyrus scrolls and packets, limestone or ceramic ostraca, wooden writing boards, monumental stone edifices, and even coffins. Texts preserved and unearthed by modern archaeologists represent a small fraction of ancient Egyptian literary material. The area of the floodplain of the Nile is under-represented because the moist environment is unsuitable for the preservation of papyri and ink 0inscriptions. On the other hand, hidden caches of literature, buried for hundreads of years, have been discovered in settlements on the dry desert margins of Egypt. Read more...
Selected picture
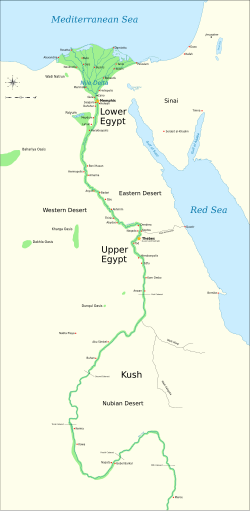
Credit: Jeff Dahl
In antiquity, Ancient Egypt was divided into two lands: Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. To the south, it was bounded by the land of Kush, and to the East, the levant. Surrounded by harsh deserts, the river Nile was the lifeline of this ancient civilization.
Did you know...
... that the pyramid complex of Userkaf is organized on a north-south axis and nobody knows why?
News
5th September 2018. At Lisht was discovered a rock cut tomb of an Egyptian official, dating to the 12th Dynasty. Rock-cut Tomb in a 4000-year-old Elite Cemetery Discovered
26th August 2018 An Egyptian team under the direction of Fahima El Nahas discovered several Ptolemaic tombs in the west of Alexandria. Ptolemaic rock-cut tombs discovered in Alexandria
August 2018: in the tomb of the mayor of Memphis Ptahmose who dates around 1300 BC was found well preserved cheese, more than 3000 years old. [1]
WikiProjects
Selected biography
Philitas of Cos (c. 340–c. 285 BC) was a scholar and poet during the early Hellenistic period of ancient Egypt. A Greek associated with Alexandria, he flourished in the second half of the 4th century BC and was appointed tutor to the heir to the throne of Ptolemaic Egypt. He was thin and frail; Athenaeus later caricatured him as an academic so consumed by his studies that he wasted away and died.
Philitas was the first major writer who was both a scholar and a poet. His reputation continued for centuries, based on both his pioneering study of words and his verse in elegiac meter. His vocabulary Disorderly Words described the meanings of rare literary words, including those used by Homer. His poetry, notably his elegiac poem Demeter, was highly respected by later ancient poets. However, almost all his work has since been lost. The 1st century AD rhetorician Quintilian ranked Philitas second only to Callimachus among the elegiac poets. Philitas' influence has been found or suspected in a wide range of ancient writing; Longus' 2nd century AD novel Daphnis and Chloe contains a character likely named after him. Hermesianax wrote of "Philitas, singing of nimble Bittis", and Ovid twice calls her "Battis". It is commonly thought that Bittis or Battis was Philitas' mistress, and that Hermesianax referred to love poetry; another possibility is that her name connoted "chatterbox", and that she was a humorous personification of Philitas' passion for words. Almost all that he wrote seems to have disappeared within two centuries, though, so it is unlikely that any writer later than the 2nd century BC read any but a few of his lines.
General images
The following are images from various ancient Egypt-related articles on Wikipedia.
M. who that mo fo looking at ?
K11. chill babe mans not worth it,
I got you, your mine.
M. #Facts
Greywacke statue of the pharaoh Menkaure and his queen consort, Khamerernebty II. Originally from his Giza temple, now on display at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
Related portals
Main topics
Symbols
Notable Pharaohs
Religious concepts
Categories
► Kemetism
Recognized content
Recognized content
Featured articles
Good articles